Home
3Tpy
General
3Tpy - Telnet Testing Tool is a simple Python application which main purpose is creation and execution of tests or configuration over telnet protocol.
License
3Tpy is released under GNU GPLv3 license http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html
Test approach
3Tpy test scenario is a set of test cases. Each test cases is represented by 3 values:
+ command -> String which is sent over telnet to system under test
+ expected -> String which is compared with telnet output. Test case result is based on this comparison
+ stop on error -> Boolean which is ignored if equals to false. If true and test case failed due to comparison of expected value with output then test scenario is stopped

Installation
The only precondtition is to have Python 3.2.3 or 3.3.0 installed (At least these version are available at the moment I am writing this. Hopefully 3Tpy will work with later Python releases). @ Linux it might be additionally required to install Python tk library to run GUI (@ Windows, tk is available by default after installing Python). You can download Python from official webpage http://www.python.org/download/. In case of Ubuntu, you can use APT, for example:
sudo apt-get install python3
sudo apt-get install python3-tk
After Python is properly installed, simply download and unzip 3Tpy. It can be started in gui and console mode.
Usage
First you need to create a test scenario consisting of 1 or more test cases. To do it, you need to open 3Tpy in GUI mode (of course you can create xml file manually but it is pointless). You can start from scratch by adding empty test cases to a new test scenario or you can use one of example files from exampleInput directory. Definition of a test case is described in test approach chapter. To make everything work properly, also telnet options must be configured:
+ ipaddress -> IP address of system under test
+ username -> system under test telnet login
+ password -> system under test telnet password
+ loginprompt -> prompt which is shown while system asks for a login, for example login:
+ passprompt -> prompt which is shown while system asks for a password, for example password:
+ regularprompt -> prompt which is shown every time after command is sent, for example user@system:~$
Test scenario can be started by pressing Run! button. Log is shown in GUI and saved to default location. If you want to run a test scenario in non-gui mode, test scenario must be saved into xml file. A single test scenario corresponds to 1 xml file.
Command line parameters
There are few options while starting an application:
+ gui mode requires no parameters, for example python 3Tpy.py
+ non-gui mode -> -n test_scenario_file_name, for example python 3Tpy.py -n exampleInput\exampleTestScanrio.xml
+ non-gui mode with custom log name -> -n test_scenario_file_name -l custom_log_file, for example python 3Tpy.py -n exampleInput\exampleTestScanrio.xml -l mynewlogfile
Gui
3Tpy GUI is quite intuitive (at least I hope so).
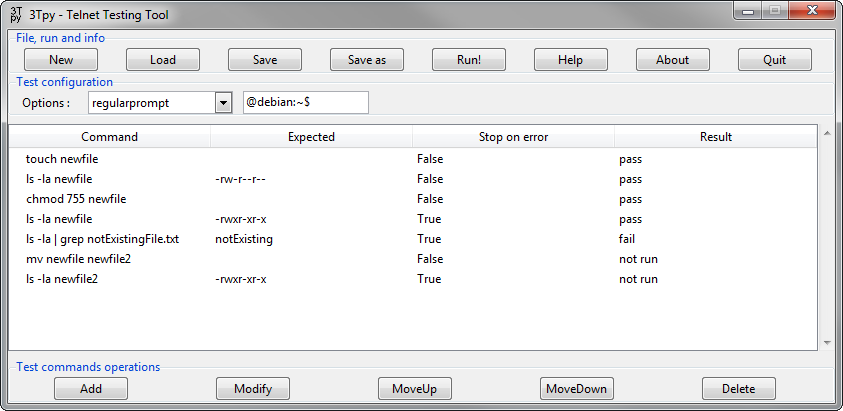
Top buttons are responsible for loading and saving test scenario files, running or creating new test scenario, dipslaying information and closing program. Test configuration area makes it possible to apply telnet related configuration. Test scenario tree (it looks like a table but it is TreeView widget in fact) is a graphical representation of all test cases related to active test scenario. In addition to all test case parameters, it also shows results if run in GUI mode. Finally, bottom buttons modify test cases which are visible in a test scenario tree.
Logs
By deafult, there is a text log created in the same directory from which 3Tpy was started. In the end of a test run it is also converted into html format.

Default log name and location can be changed by using -l parameter in non-gui mode. In gui mode, log is additionally presented in a window and updated in real time.

